Knowledge
Provide an overview of terms and concepts related to home energy.
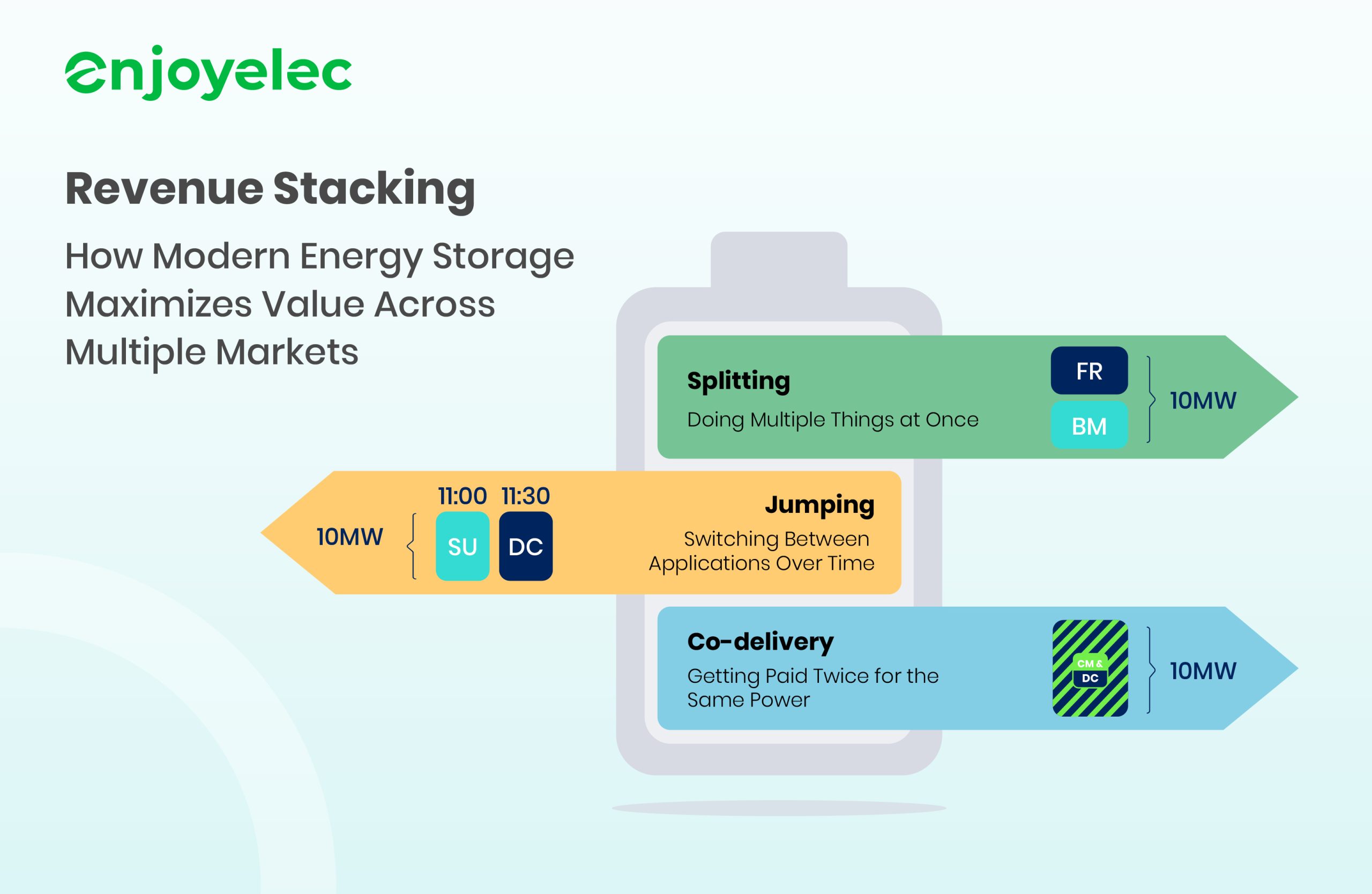
Battery energy storage is increasingly recognized as a key enabler of modern power systems. Yet the financial success of storage projects often depends on more than simply installing the hardware. The real value lies in how intelligently that capacity is used. This is where revenue stacking comes into play. Revenue stacking refers to the strategy of maximizing the economic value of energy storage asset by capturing multiple revenue streams across different markets, services, or time periods.
Without active grid flexibility, enabled by smart integration of solar, storage, and intelligent control, homes and businesses are exposed to unpredictable bills and potential reliability risks.
- Tags: enjoyelec App
Your Home's Energy, Perfectly Clear at a Glance: Introducing the Redesigned enjoyelec App for iPad and Android Tablets
- Tags: Controller Lite
Meet Controller Lite: The focused, future-ready HEMS designed with extraodinary grid compliance.
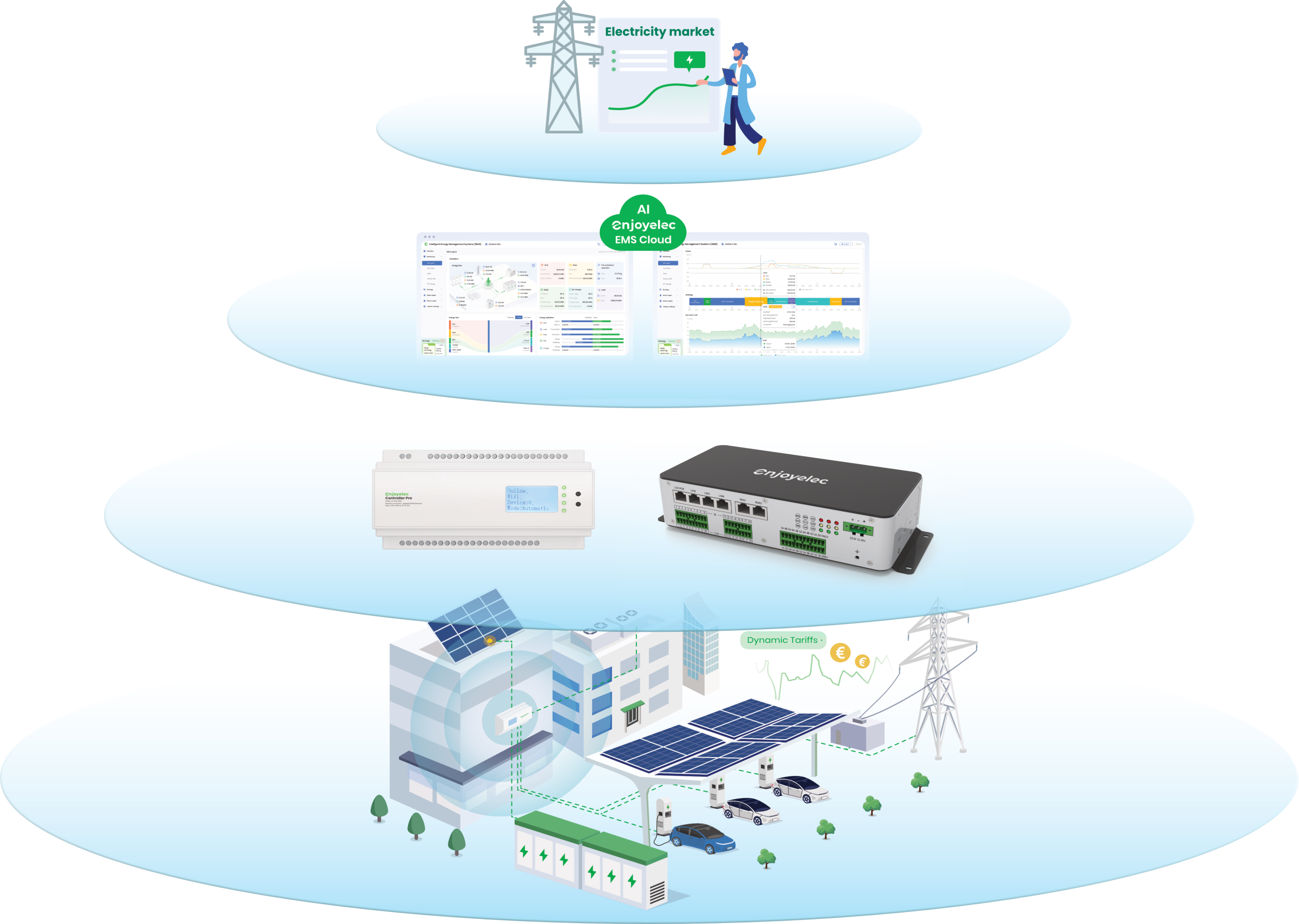
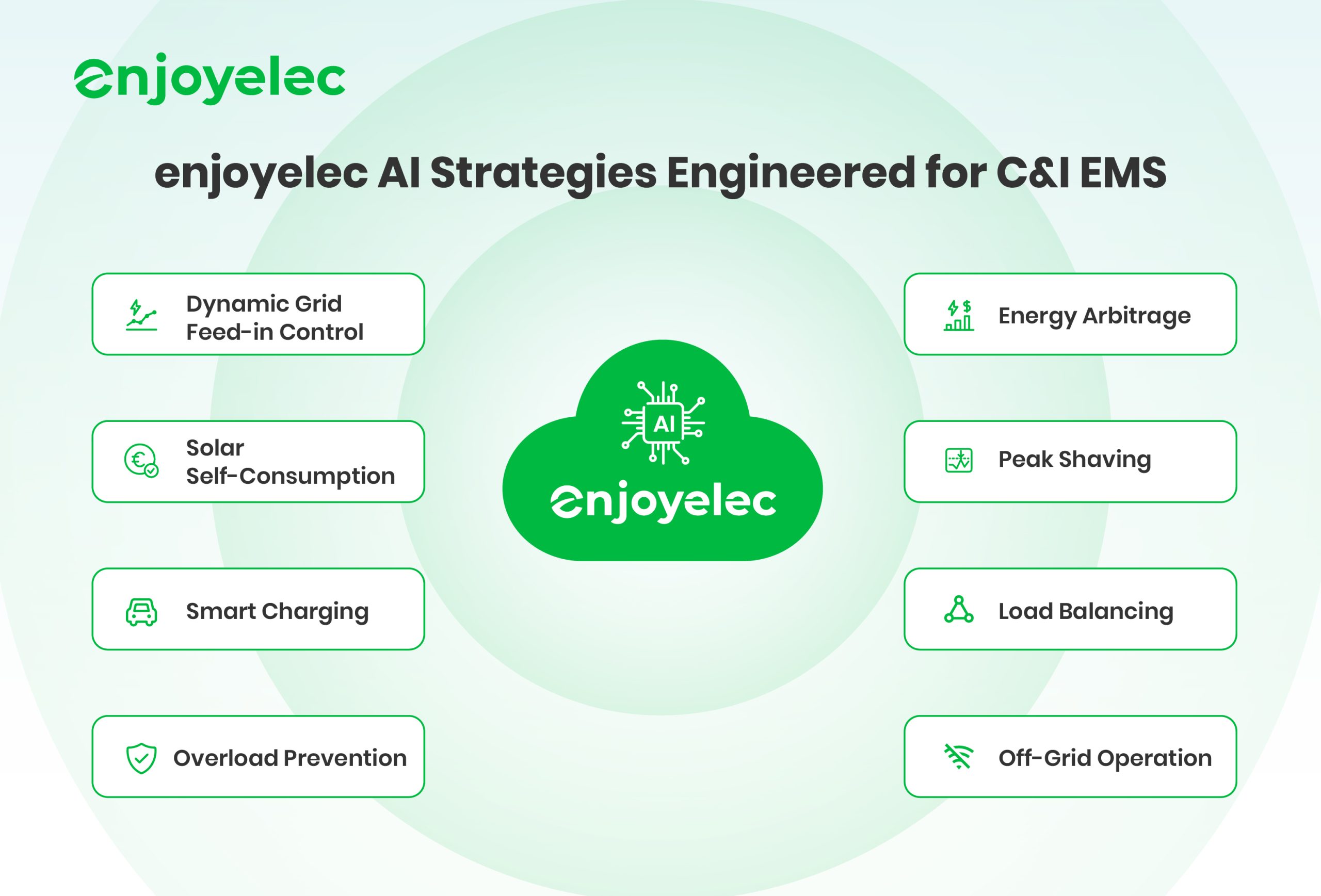
The solution is intelligent, data-driven orchestration—the core role of an Energy Management System (EMS). It bridges distributed resources, flexible loads, and dynamic markets to build resilience, unlock revenue, and ensure sustainability. enjoyelec AI-powered EMS delivers targeted, high-impact value in four core scenarios:
The key to harnessing this collective power is smart management, or, more precisely, the Home Energy Management System (HEMS).
The key to harnessing this collective power is smart management, or, more precisely, the Home Energy Management System (HEMS).
Many homeowners today are making a significant investment in clean energy assets like rooftop solar, home battery, and EV chargers. But (as this Dutch customer discovered),simply having the hardware is obviously not enough
What’s the Difference Between Self-Consumption and Self-Sufficiency? The two terms are often used interchangeably, but they represent two different stages in your energy journey.